Javascript Basics tutorial
Learn JavaScript
Javascript Table of Contents
- Introduction to JavaScript.
- Data types in JavaScript
- Types of operators in JavaScript:
- Getting started with JavaScript
- Arithmetic Operators
- Conditional Statements
- Looping Statements
- How to check errors in JavaScript
Introduction to JavaScript.
JavaScript is a one of the scripting languages. Used to perform client-side calculations and validations on form data.
Basically, there are 2 types of JavaScript.
- Client side: To perform validations, some calculations at client side.
- Server side (SSJS) : To perform some manipulations on the server-side, and allowing applications to communicate with a database. etc.,
Ex:Node.
Data types in JavaScript
JavaScript is a loosely typed language. It means it can store different types of data each time. The type is dynamic. Its type is decided, the value that it is storing.
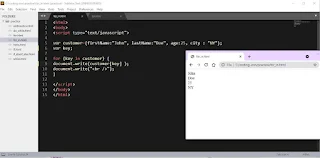
Variable: A variable is a memory location name and used to store a small piece of data for later use. Variable starts with var keyword, but it is optional.
example:
var number=5;
var customer_name="John";
var age= 33;
var city= "Delhi";
Types of operators in JavaScript:
- arithmetic: [+, -, *, /, %]
- relational: [>, <, >=, <=, !=, ==]
- logical:[&&, ||, !]
- increment: [++]
- decrement: [--]
JavaScript Conditional Statements
Conditional statements generally used in decision-making. By comparing two values, it chooses the block /statement to execute.
- if
- if..else
- if....elseif..else
JavaScript Looping Statements
Loop : Looping
statements are used to repeat a certain number of lines until a given
condition is true. In JavaScript, there are 4 types of loops available.
- while
- do-while
- for
- for/in
Getting started with JavaScript
To start with JavaScript, no coding knowledge required. If you know HTML, that will make things easier.
JavaScript's code will be written inside the script tags <script> ... </script> in the HTML page.
Every browser contains a JIT(Just In Time). It is an inbuilt compiler, to compile(check for errors) JavaScript.
Let's see how to run the first JavaScript program...
Example:
Hello.html
<html>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
document.write("Hello World!");
1. Create a folder practice
2. Create a file called Hello.html using any editor of your choice. Even windows notepad also works, and save it in practice folder.
Here I am using sublime text editor. You can download it, from this link.
Now your code looks as given below picture:
Next, open program in browser.
Formatting Text using HTML in JavaScript
Using HTML tags, text can be formatted. The below program demonstrates how to use HTML tags in JavaScript.
example2:
Hello.html
output
Comments in JavaScript:
Commented line are ignored by compiler.
To comment a single line you use: // (double forward slash) as I added in the above program.
Example:
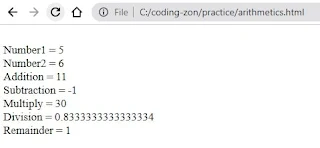
Arithmetic Operators:
Example:
<html>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
document.write("<br>Addition = " + addition );
document.write("<br>Subtraction = " + subtraction );
document.write("<br>Multiply = " + multiply );
document.write("<br>Division = " + division );
document.write("<br>Remainder = " + remainder);
</script>
</body>
</html>output
JavaScript Conditional Statements:
Using if statement in JS
Examples:
<html>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
a = 15;
b = 16;
document.write("<br>");
{
document.write(a+" is greater");
}
else
{
document.write(b+" is greater");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>output
if..else-if in JS
<html>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
{
document.write(" Grade A");
}
else if(score >= 60 && score < 800)
{
document.write(" Grade B");
}else
{
document.write(" Grade C");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>output
MenuTop ↑
Switch Statement In JS
A switch statement is a multi conditional branching statement. One value compared with multiple case options. It prints the case block, which is matched with passed value, and comes out of the switch block using break.
<script type="text/javascript"> var grade='A'; switch (grade) { case 'A': document.write("Good job<br />"); break; case 'B': document.write("Pretty good<br />"); break; case 'C': document.write("Passed<br />"); break; case 'D': document.write("Not so good<br />"); break; case 'F': document.write("Failed<br />"); break; default: document.write("Unknown grade<br />"); } </script>
JavaScript Looping Statements:
While Loop In JS
While takes the condition and repeats a block of statements until the condition is true.
Once the condition becomes false, it stops repeating, and comes out of the loop.
syntax:
while(condition) { statement1; statement2;
... statement n; }
example:
<html>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
i=0;
while(i <= 5)
{
document.write(i);
document.write("<br>");
i++;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
output
Do-while in JS
It is similar to while. The difference is, It runs the loop first, and then the condition is checked.
syntax:
do { statement1; statement2;... statement n; }
while(condition);
example:
<html>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript"> </script>
</body>
</html>output
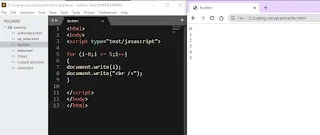
For Loop in JS
For-Loop, basically used with arrays. For statement divided into 3 parts.
Initialization, condition, incrimination.
syntax: for (initialization;condition;incrimination)
{
statement1;
statement2;...
statement n;
}
example: <html>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">for (i=0;i <= 5;i++)
{
document.write(i);
document.write("<br />");
}</script>
</body>
</html>output
For/in Loop in JS
For..In is another loop in JavaScript used with array objects.
Example: output
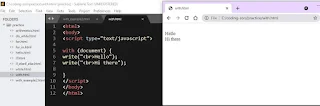
with keyword
With is a kind of block. It takes any object as parameter, and all the
methods available in that object are accessible to that block. In the following example, write
method is used without specifying object name(document) before it.
Example: }
output
Example2:
</script>
</body>
</html>
output
How to check errors in JavaScript
- right click on browser window and select inspect.
- Next, select console tab for error details.












Comments
Post a Comment