Learn SQL Queries Part2
Learn SQL Queries using MySQL Database Part-2
←Part-1
In a previous blog, we have gone through the introduction of RDBMS and SQL Language. This article lets you know how to work with databases using different types of SQL Queries. As we discussed earlier, SQL Queries are grouped into 3 categories. In this tutorial, we are going to learn each of them in detail.
Table of contents
- DDL Queries
- DML Queries
- DCL Queries
1. DDL Queries
TopMenu
1. Creating command:
Used to create database and tables
CREATE Database <Database -name>
CREATE Database SampleDB
syntax:
CREATE TABLE <Table-name> (
col1 data_type(size),
col2 data_type(size),
col3 data_type(size));
example:
CREATE TABLE employees (
empno int,
empname varchar(50),
dept varchar(50),
salary int );Executing Queries:
To run the queries, use PhpMyAdmin Tool in XAMPP, or any other tool that supports MySQL.
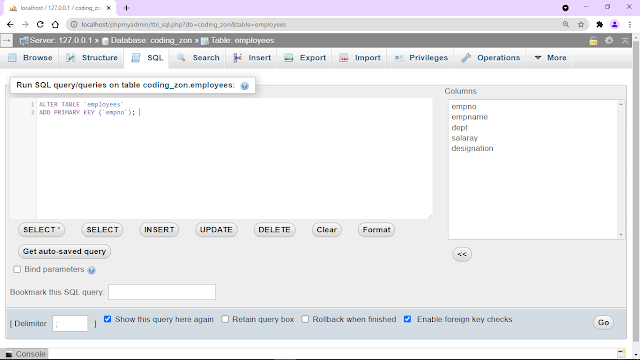
Open SQL tab and copy and paste the query and click on Go button as shown in picture.
To know how to use PhpMyAdmin tool visit this tutorial
How to run Query view the Demo
MenuTop
2. Alter Command:
Used to change structure of database and tables. Such as changing field name, width, datatype etc.
example:
ALTER TABLE employees ADD COLUMN designation varchar(15);
example2:
ALTER TABLE `employees` ADD PRIMARY KEY (`empno`);
3. Drop Command:
Used to drop database and tables
example:
DROP table student_details;2. DML Queries.
Statements for to work with table data. Using these 4 commands, we can manage data.
- SELECT
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
1. SELECT Statement:
Used to select specific or all rows and columns from the tables.
Selecting all columns:
SELECT * FROM employees
Selecting specific column:
SELECT empno, empname, salary FROM employees
Selecting specific columns and rows:
To select specific rows WHERE clause is used. To filter data
WHERE Clause is combined with Relational and Logical operators:
Relational Operators( >, <, >=, <=, ==, !=)
Logical Operators( and , or, not) Examples:
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary >=30000;
SELECT empno, empname, salary FROM employees WHERE empno < 105; SELECT empno, empname, salary FROM employees WHERE empno < 100 and dept='finance'
LIKE operator: To search for a specific pattern
SELECT empno, empname, salary FROM employees WHERE empname LIKE 'J%';
WHERE clause can be used with SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE
Menu↑Top
2. INSERT Statement: Inserts new records into the table:
Syntax:
INSERT into <tablename> VALUES(val1,valu2,val3,val..N); if no columns specified after table name, that means you need to provide values for all fields as shown below..
Example:
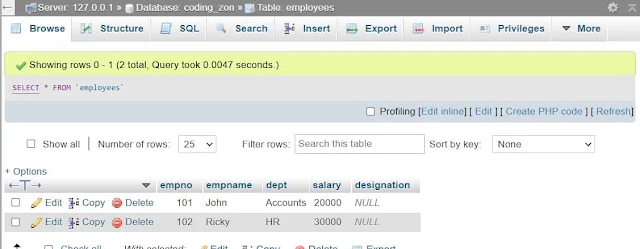
INSERT into employees VALUES(101, 'John', 'Accounts',20000,'Manager');
INSERT into employees VALUES(102, 'Ricky', 'HR',30000,'Clerk');
Output
If empno is set as autoincrement, then no need to provide value for empno.
INSERT into employees VALUES('sonu', 'IT',30000,'developer');
syntax:
INSERT into <tablename> (col1,col2) VALUES(val1,valu2);
example:
INSERT into employees(empname, salary) VALUES('mona',16000);
example2:
INSERT into employees(empname, dept, salary) VALUES('Sunny', 'computers',35000);
3. UPDATE Statement: updating old values with new values.
UPDATE <tablename> set col1=val2 where col1=val1;
UPDATE employees set empname='newname' where empname='oldname'
4. DELETE Statement: Removes a row/rows from the table.
Syntax:
DELETE from <tablename> where col1=val1;
Example:
DELETE from employees where empno=102;
Goto Menu
Aggregation Commands: These commands works on total records of a table.
- sum
- count
- min
- max
- avg
Table: employees
empno salary
101 20000
102 30000
example:
SELECT SUM(salary) FROM `employees`o/p:
SUM( salary )
50000
count(*): return total no of records:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM `employees`o/p:
2
MIN:
example:
SELECT MIN( `salary` ) FROM `employees`
o/p:
min(`salary`)
20000
MAX:
example:
SELECT MAX( `salary` ) FROM `employees`
o/p:
max(`salary`)
30000
AVG(average):
example:
SELECT AVG( `salary` ) FROM `employees`o/p:
AVG( `salary` )
25000
sorting
example: SELECT * FROM employees ORDER BY `salary` ASC;
SELECT * FROM employees ORDER BY `salary` DESC;
Move to Top Menu
3. DCL Queries.
- Grant :
Adds the permissions to users on a particular object in the database. - Revoke:
Removes permissions on a particular object in the database for that user.
Examples:
Database Administrator will create users and manages the permissions on databases using grant and revoke commands as follows:
Creating User:
CREATE USER 'jenny'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'mypass123';
Granting permissions to user on various databases;
GRANT ALL ON mydb1.* TO 'jenny'@ 'localhost'; GRANT SELECT ON mydb2.invoice TO 'jenny'@'localhost'; GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO 'jenny'@'localhost' WITH MAX_QUERIES_PER_HOUR 70;
Revoking Permissions on Insert from User:
REVOKE INSERT ON *.* FROM 'jenny'@'localhost';
CONCLUSION
In this article, I have discussed the types of SQL commands ( DDL, DML, and DCL ) in MySQL using various examples.
Move to Top





Comments
Post a Comment